Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Chemical Properties of Acids, Reactions of Acid with Metals, Reaction of Zinc with Dilute Sulphuric Acid, Reactions of Bases with Metals, Reaction of Zinc with Sodium Hydroxide, Reactions of Metal Carbonates with Acids, Reactions of Metal Hydrogen Carbonates with Acids, Neutralisation Reactions, Reactions of Metallic Oxides with Acids, Reaction of Copper(II) Oxide with Dilute Hydrochloric Acid, Reactions of Non-metallic Oxides with Bases, Reaction of Carbon Dioxide with Lime Water & Nature of Non-Metallic Oxide etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases
Aqueous solution of is
of solution gets completely neutralized with of solution. What volume of the same solution will be required to neutralized of the same solution-
Aqueous solution of is
Zinc reacts with solution to produce
Which of the following pair of compounds cannot exist together in a solution?
A piece of charcoal was heated over the flame of the burner. When it starts burning it is immediately dipped into a boiling tube containing water. Now, this solution is transferred to another boiling tube and a piece of litmus paper is dipped into it. What will be the observation?
and belong to period of the periodic table. Out of these, the acidic oxide is formed by
Select the organic acid from the following:
Glacial acetic acid is
An equal volume of molar hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid is neutralised by dilute solution and and of heat are liberated. Which of the following is true?
What will be the products when an acid reacts with metals?
A few drops of ethanoic acid were added to solid sodium carbonate. The observation made was that
of an organic dibasic acid required of solution to complete the neutralisation. The molecular mass of the acid will be -
What happens when dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings?
What is the chemical formula of milk of magnesia?
Which is not correct?
The solution Y in the burette is slowly dropped onto the solution X in the flask as shown. The pH change obtained against the added volume of Y is given in Graph -1.
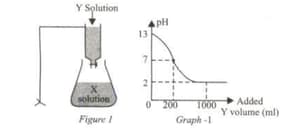
According to this,
(i) Solution X is acidic.
(ii) when 150 mL of solution Y is added, the pH is >7.
(iii) Complete neutralization occurs when 200mL of solution Y is added.
Which of these judgments is correct?
Aqueous solution of H2SO4 is added dropwise in KOH solution as shown
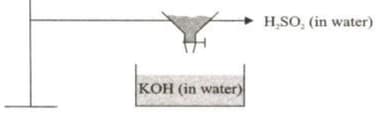
Which statements given below are correct?
(i) The equation for the reaction taking place in the vessel is
(ii) Complete neutralisation occurs when a solution containing 1 mole of H2SO4 is added.
(iii) The net ion equation for the reaction taking place in the vessel is
Some statements are given for the process:
Acid + BaseX +
(i) It is a neutralization reaction.
(ii) Acid: HNO3, Base: NaOH
(iii) If X: NaBr, Acid: HBr, Base: NaOH
Which of these statements is/are correct?
Which of the following is not sufficient alone to prove that an aqueous solution is acidic?
(i) Conducting electric current
(ii) Marble abrasion
(iii) Contains H3O+ ion
(iv) Cation concentration higher than anion concentration
